Topic we have discussed last tuesday January 06, 2015 is all about genetics in which it invokes about who is the father of Modern Genetics. Honestly, we're thinking about it and it takes time for us to know. So our teacher explains who is the father of Modern Genetics and simply his experiments. He is Gregor Johann Mendel who discovered the fundamental principles of genetics by breeding garden peas. He is also an Augustinian friar or priest and presented his paper Versuche uber Pflanzenhybriden which talks about Plant Hybridization. He also establish momentously that traits are pass from parents to their offspring in mathematically predictable way such as the punnet square.We are curious why in many organisms, Mendel choose to breed plants especially the garden peas (Pisum Sativum).
Mendel chose to experiment with peas because they possessed five importantant qualities. Garden Peas have both stamens and carpal, short generation of time, it can produce many offspring, easy to care for and it has many paired characteristics.This considerations enter into the choice of organisms for any piece of genetic research. The trait that Mendel studied are listed below:
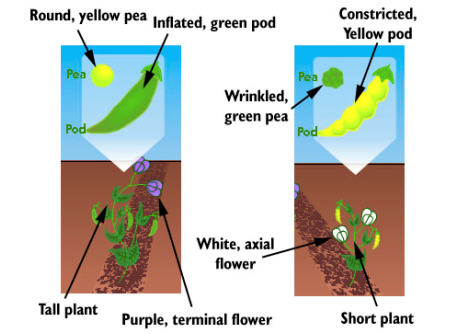
- Form of ripe seeds(R)- smooth or wrinkled
- Color of seed albumen(Y)- yellow or green
- Color of flower(P)-purple or white
- Form of ripe pods (I) – inflated or constricted
- Color of unripe pods (G) – green or yellow
- Position of flowers (A) – axial or terminal
- Length of stem (T) – tall or dwarf
It was not by accident that it became his experimental plant. Even from the start, he was already aware that garden peas must be used in order to avoid the risk of questionable result. And Gregor Johann Mendel uses a test cross in which homozygous recessive with dominant phenotype but unknown genotype can determine the identity of the unknown allele.

Another is the use of Punnet square that predicts the gene combination of parents who is unknown. There are also Mendelian Traits either dominant or recessive wherein most of my traits are in dominant such as free earlobe, has finger hair and normal thumb. And some Mendelian traits are Achondroplasia a dominant trait that is a form of short-limbed dwarfism, Xeroderma pigmentosum, or XP, an autosomal recessive genetic disorde of DNA repair in which the ability to repair damage caused by ultraviolet rays and Polydactyly an autosomal dominant mutation in which a person has more than five fingers per hand or five toes per foot.
After this I've learned a lot especially the process of breeding plants like what Mendel do through the selective cross breeding in which garden peas can either self pollinate or cross pollinate with another plant where it was the basis of his conclusion about the nature of genetic inheritance. And also the use of punnet square where it gives the correct probabilities for the genotype outcomes for independent crosses where the probability of copies of each parent allele is independent and that it is the representation of Mendelian inheritance. Concepts which I think related to this topic is about heredity and variation in which it talks about genes which is the basic unit of inheritance including alleles( dominant or recessive) or simply form of genes. And the use of punnet square that could show the genotype of two individuals. So strategies I will do to understand this is to surf the internet, read books and try to understand it clearly through example problem like this:
- In purple people eaters, one-horn is dominant and no horns is recessive. Draw a Punnet Square showing the cross of a purple people eater that is hybrid for horns with a purple people eater that does not have horns. Summarize the genotypes & phenotypes of the possible offspring.
Genotypes of Offspring Phenotype(s) of Offspring
50% hybrid (Hh) 50% one horn
50% homozygous recessive (hh) 50% no horn
H = dominant allele for one horn
h = recessive allele for no (zero) horns
A purple people eater that is "hybrid" has one of each letters (the definition of hybrid), so that parent is "Hh". A purple people eater without horns has the recessive phenotype and the only way to have a recessive phenotype is to have a homozygous recessive genotype, which is 2 lowercase letters, "hh".
So our cross for this question is: Hh x hh

Thank you!!!!I hope you like my blog.